Everyone talks about how terrifying cancer cells are because they devour normal cells and jeopardize people's health. But what they may not know is that cancer cells are not invincible. Once you grasp the key points, subduing them is completely feasible!
When it comes to cancer treatment, many people's first thoughts go to radiation, chemotherapy, surgery, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. However, these treatments either have significant side effects or fail to meet treatment criteria. What's more important is that, while killing tumor cells, they also harm normal cells, leading to various complications.
In the past decade, "precision + minimally invasive" has become a hot topic in tumor treatment. Currently, Royal Lee Cancer Center in Guangzhou can carry out precise minimally invasive intervention therapy for various benign and malignant tumors, as well as tumor-related complications. Today, we'll first introduce a minimally invasive treatment that is widely applicable, low in trauma, with few complications, quick recovery, and can be repeatedly applied—the microwave ablation technique.
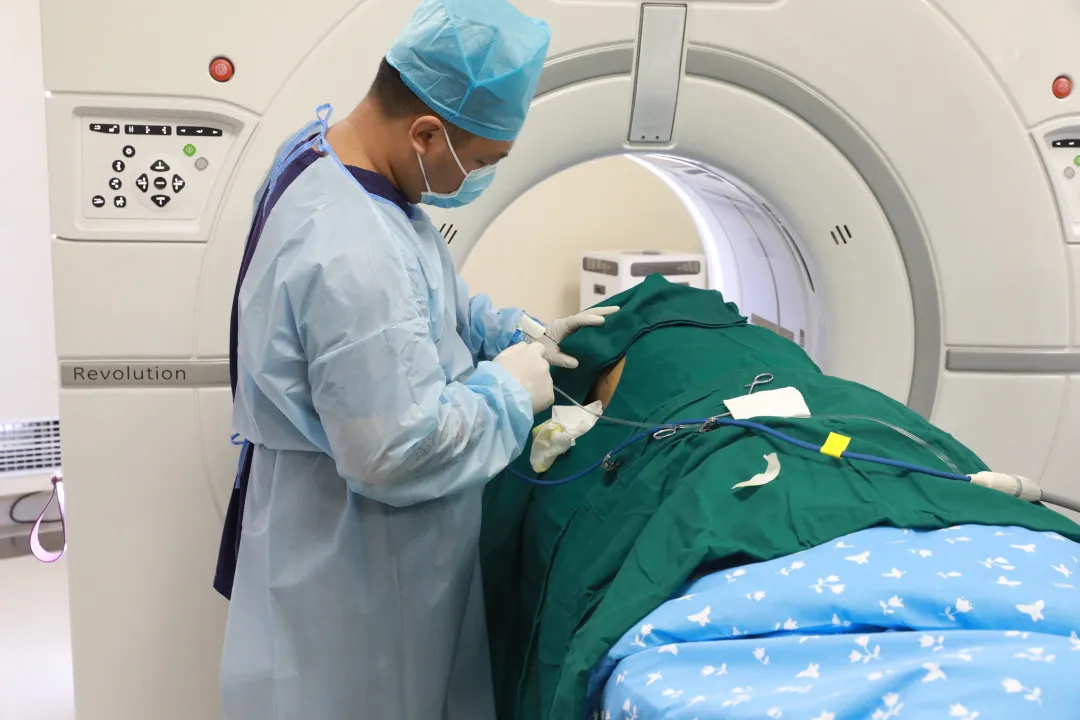
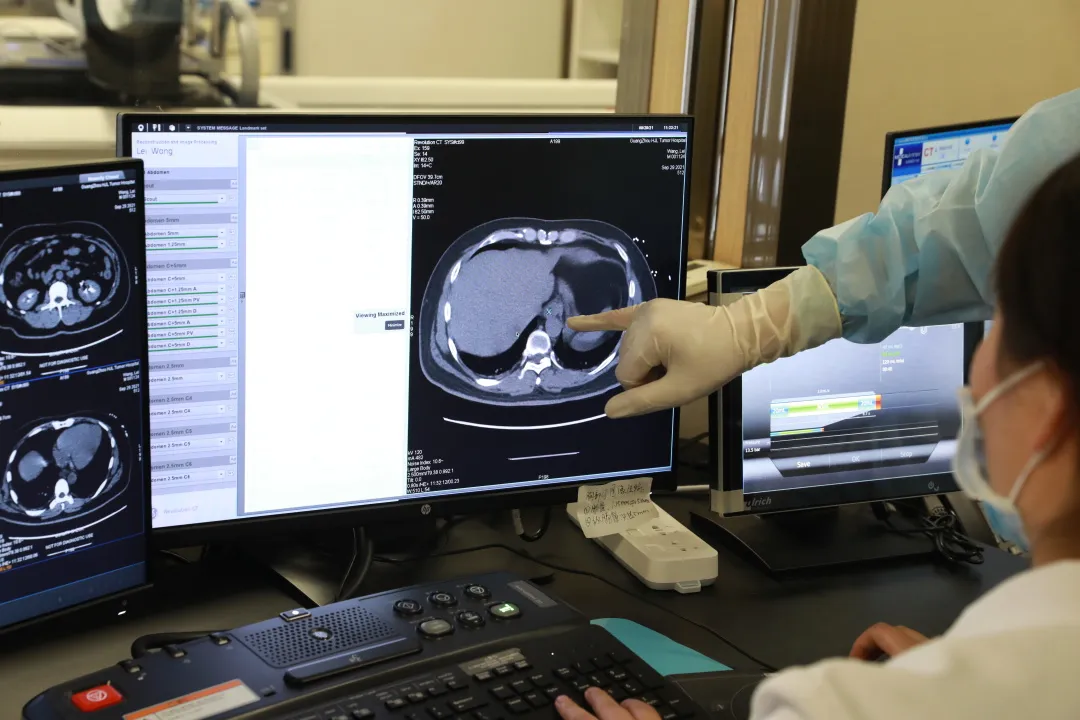
What is Microwave Ablation?
Microwave ablation is actually a type of minimally invasive thermal ablation. The specific treatment method involves guiding a specially designed microwave needle through the skin directly into the tumor area under the guidance of ultrasound/CT imaging equipment.
At this point, the tip of the microwave needle contains a "miniature microwave oven" heating zone about 1 centimeter long. The microwave magnetic field released can cause high-frequency repetitive rotational motion of polar molecules such as water molecules and protein molecules in the tumor. The friction between polar molecules rapidly raises the temperature inside the tumor, causing the tumor to quickly undergo coagulative necrosis (tumor cells can undergo irreversible necrosis at 60°C), achieving the purpose of killing tumor cells.
Why Can Microwave Ablation "Kill" Cancer Cells?
As mentioned earlier, cancer is terrifying, but as long as you grasp its key points, defeating it with one move is possible. Microwave ablation precisely exploits the characteristic of cancer cells being sensitive to heat.
Research indicates that cancer cells have very poor heat resistance. When a certain temperature is reached, cancer cells undergo apoptosis.
Moreover, tumor tissue lacks a complete vascular structure and function. Tumor blood vessels are chaotic, with little change in blood flow and poor heat dissipation. When heated externally, a large amount of heat gathers there, causing denaturation and necrosis of tumor tissue proteins, leading to cell destruction and subsequent apoptosis.
Microwave ablation can achieve temperatures of 60°C-150°C within minutes, effectively inactivating cancer cells in a short time.
Unmissable Advantages of Microwave Ablation
With countless tumor treatment methods available, why does microwave ablation stand out and become the preferred choice for various solid tumor patients such as small liver cancer, liver metastases, abdominal and thoracic solid metastases internationally, and also regarded as a boon for early-stage lung cancer and lung nodules patients who are not suitable for or refuse surgery?
The main reason lies in the precise, safe and effective, minimally invasive, repeatable, easy-to-perform, low-cost, low patient discomfort, and high postoperative quality of life advantages of microwave ablation.
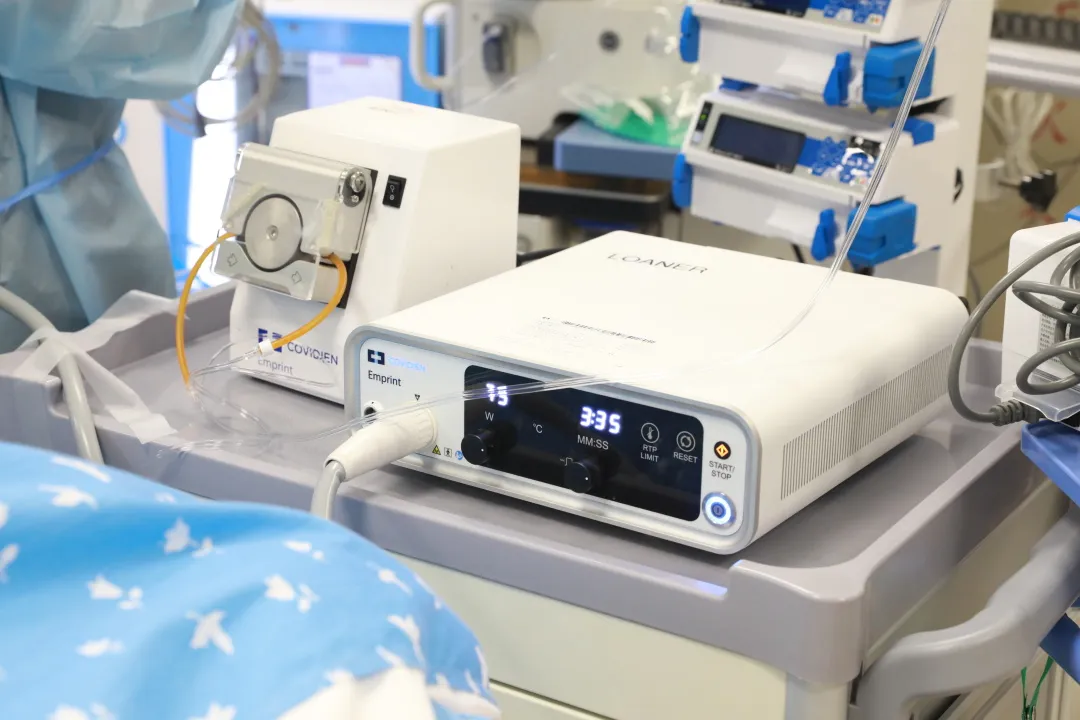


Additionally, tumor microwave ablation therapy can be combined with surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and other treatments according to the patient's actual condition to achieve the optimal treatment efficacy.
When is Microwave Ablation Suitable?
Usually, solid tumors of non-visceral organs, such as lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, liver cancer, liver and lung metastases, thoracic and abdominal solid metastases, etc., are suitable for microwave ablation due to various reasons such as being unsuitable for surgery and systemic chemotherapy.
Some patients may worry about whether the size and range of the tumor will affect their choice of this procedure. Generally, microwave ablation has no absolute restrictions on the range and size of tumors, but it is most suitable for patients with smaller, less numerous tumors, or larger solid tumors still confined to the organs.
The ideal ablation target is a single lesion smaller than 5cm or 3~4 multiple lesions smaller than 3cm. Larger lesions can also be treated with ablation, but to achieve complete lesion ablation, multiple repeat ablations are necessary, with each lesion not exceeding 3cm in diameter.
Of course, with the aging population, some elderly patients with poor cardiopulmonary function who cannot tolerate surgical resection can also choose microwave ablation to inactivate tumors under conditions that meet the requirements.
FAQ:
Q: Can tumors that recur after chemotherapy be treated with microwave ablation?
A: For some tumors that recur after chemotherapy, radiation therapy cannot be performed in situ within one year, while microwave ablation can be performed multiple times within one week.
Q: Do patients experience adverse reactions after microwave ablation?
A: After treatment, patients may experience mild reactions such as early fever, without the obvious discomfort of chemotherapy. If there are other discomforts, medical attention should be sought promptly for investigation.
